Patient assessment tools, techniques, checklists and infographics. Designed for the prehospital environment for use by event medics. Content updated regularly with the latest content always posted on our Facebook group first.
QUICK REFERENCE PAM
Download the single page quick reference guide to the patient assessment model.
Ideal for refreshing your memory or as a study aid. Can also be used in classrooms for practice.
See the full Patient Assessment Model PDF for the full explanation.
PATIENT ASSESSMENT MODEL
The Patient Assessment Model (PAM) is a proven technique for rapid, efficient review of patient conditions, illnesses and injuries in a pre-hospital environment.
This is a multipage step by step guide covering scene survey, primary survey and complete secondary survey with detailed head to toe examination points and questions.
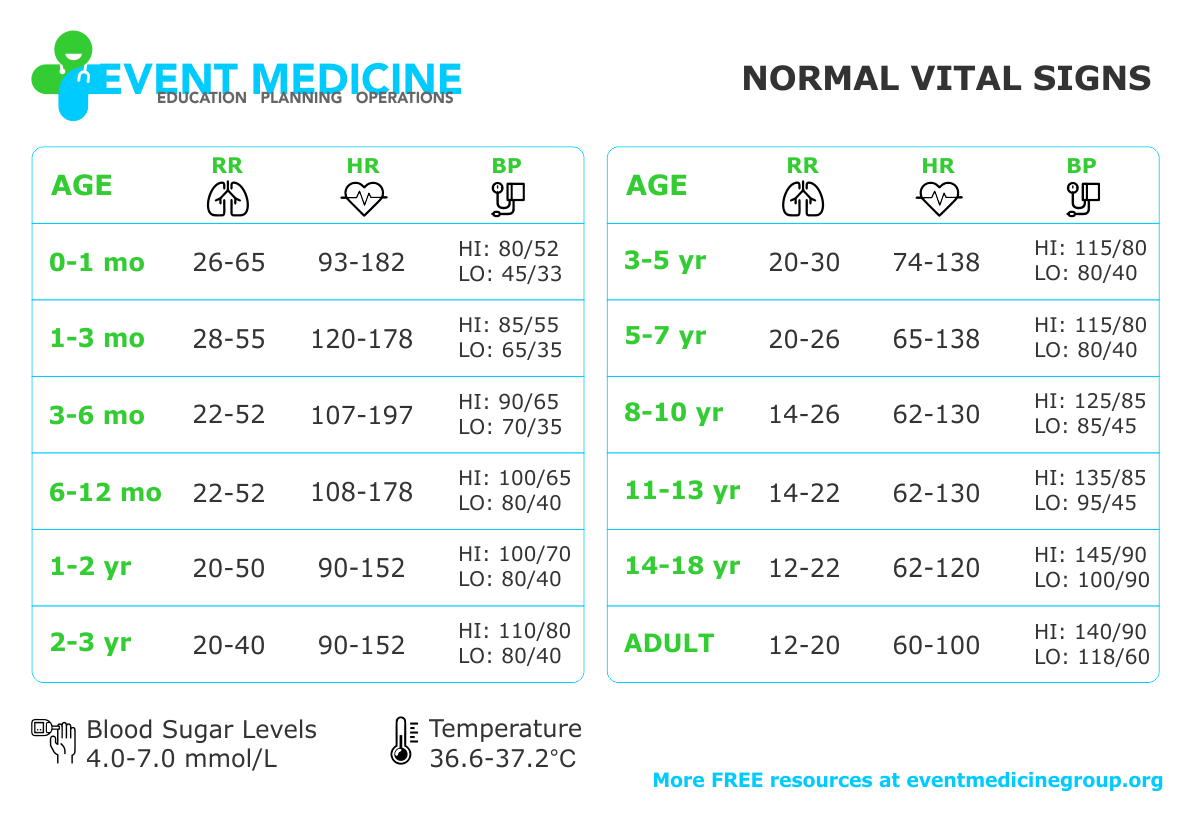
NORMAL VITAL SIGNS
Quick reference guide to vital signs. This guide shows both Normal Pediatric Vital Signs for all ages through to and including Normal Adult Vital Signs.
AVPU
Rapid level of consciousness assessment tool for use in the primary survey.
Alert - Verbal - Pain - Unresponsive
GLASGOW COMA SCALE
A structured approach using best practices to assessing a patient’s level of consciousness using the Glasgow Coma Scale.
Two resources available:
GCS chart with quick tips.
Assessment guide describing the process step by step.
APGAR
Check on the health of a newborn baby using the APGAR rating scale. APGAR is a scoring system best employed within the first 5 minutes of birth.
Remember, APGAR is a general indication of overall health only. Manage the newborn based on the signs and symptoms present.
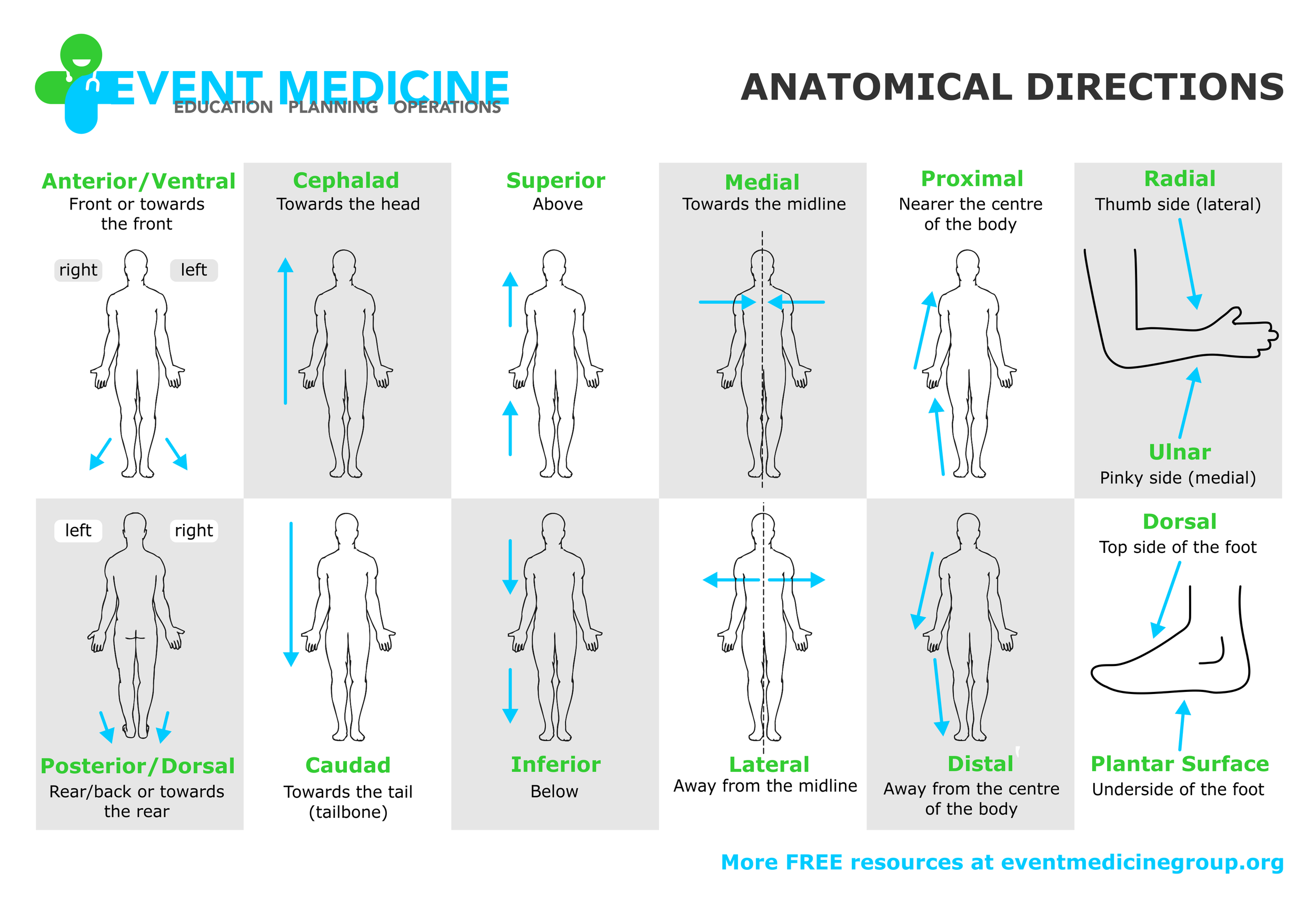
ANATOMICAL DIRECTIONS
Left/Right: the patient's left/right
Anterior/Ventral: front, or towards the patient's front
Posterior/Dorsal: back, or towards the rear of the patient
Cephalad: towards the head
Caudad: towards the tail (tailbone/base of spine)
Superior: above something
Inferior: below something
Medial: towards the midline
Lateral: away from the midline
Proximal: nearer the centre of the body
Distal: away from the centre of the body
Forearm and hand:
Radial = thumb side (lateral).
Ulnar = pinky finger side (medial).
Foot:
Dorsal = top side.
Plantar surface = bottom of the foot.
PEDIATRIC ASSESSMENT TRIANGLE
Rapid assessment tool for pediatric acuity and triaging pre-hospital.
Is the child in respiratory distress, respiratory failure, or shock?
Note the acronym TICLS
MEDICAL ABBREVIATIONS & TERMINOLOGY
Originally created in British Columbia, Canada, this document may have some regional biases. Please feel free to comment and it will be updated to be more globally relevant. It's a living document.
RESPIRATORY PATTERNS
Identify the causes behind different breathing patterns.
This chart shows respiratory waveforms based on inspiratory and expiratory patterns for medical and traumatic causes.
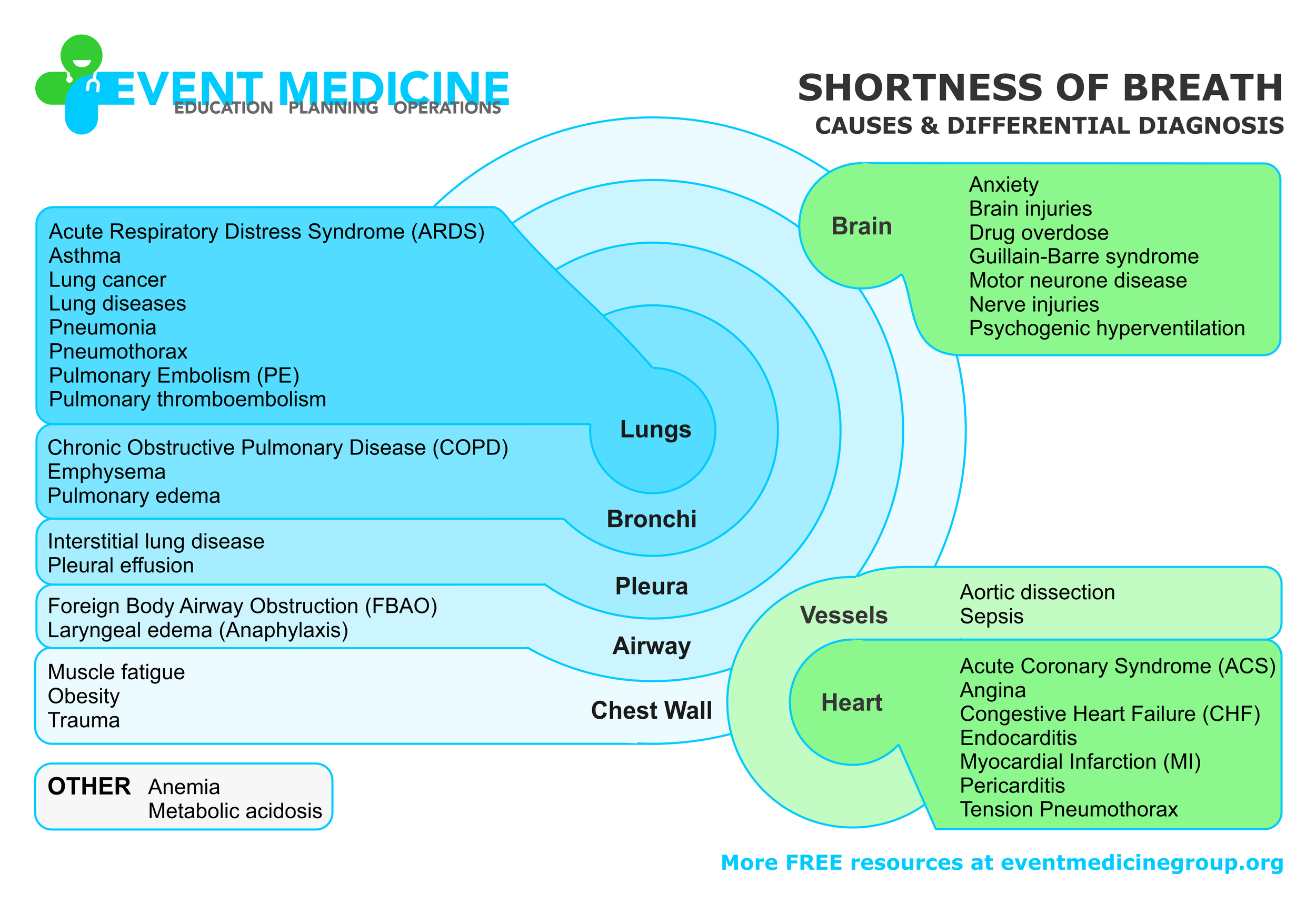
SHORTNESS OF BREATH CAUSES
Develop your differential diagnosis for SOB and breathlessness by thinking about the anatomy first. Start with the lungs and work your way outwards. Consider other areas that may be impacting the breathing such as the brain, heart, and vessels.
Download Shortness of Breath Causes & Differential Diagnosis PDF.
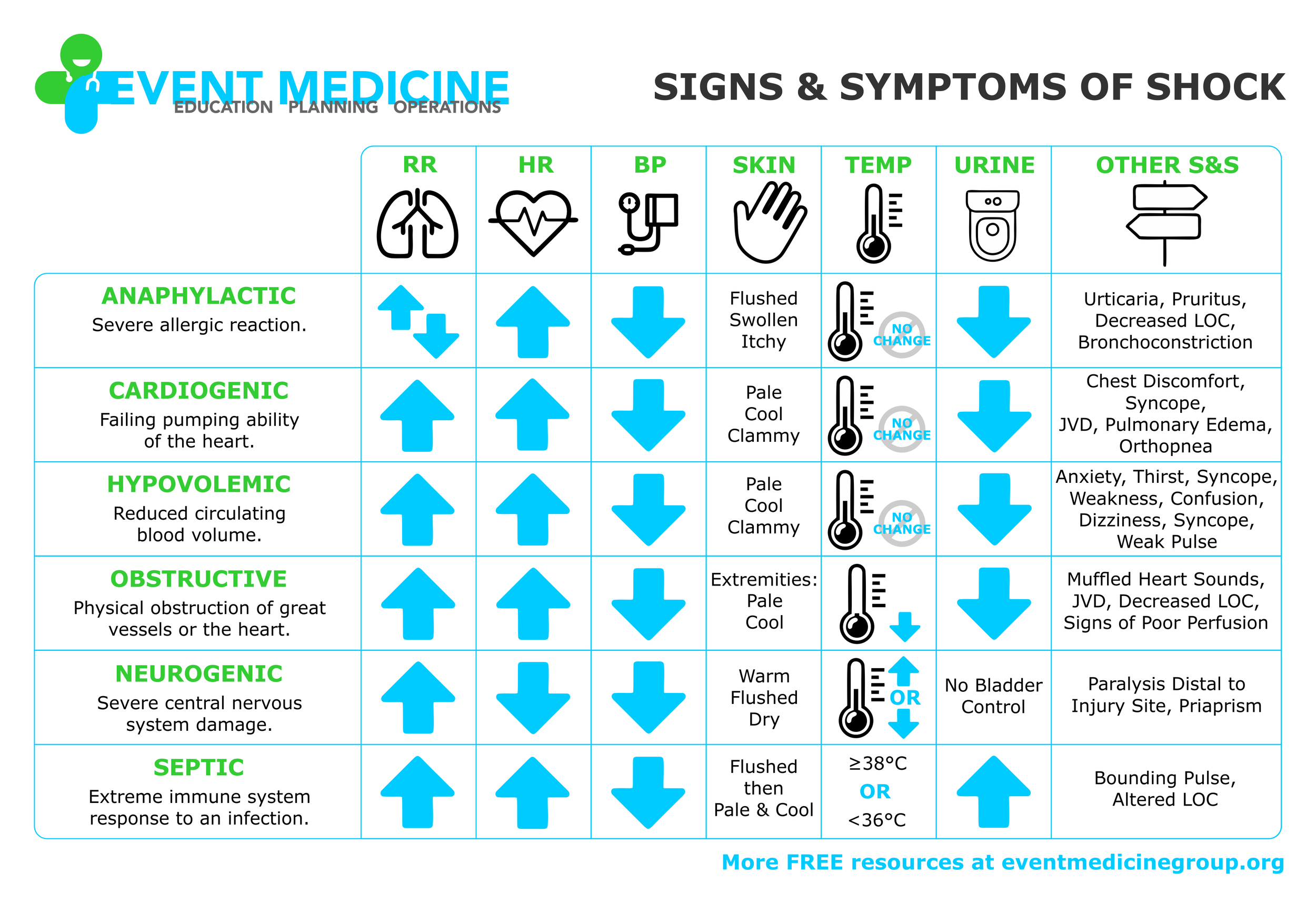
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS OF SHOCK
Learn the key signs and symptoms of six categories of shock:
Anaphylactic
Cardiogenic
Hypovolemic
Obstructive
Neurogenic
Septic
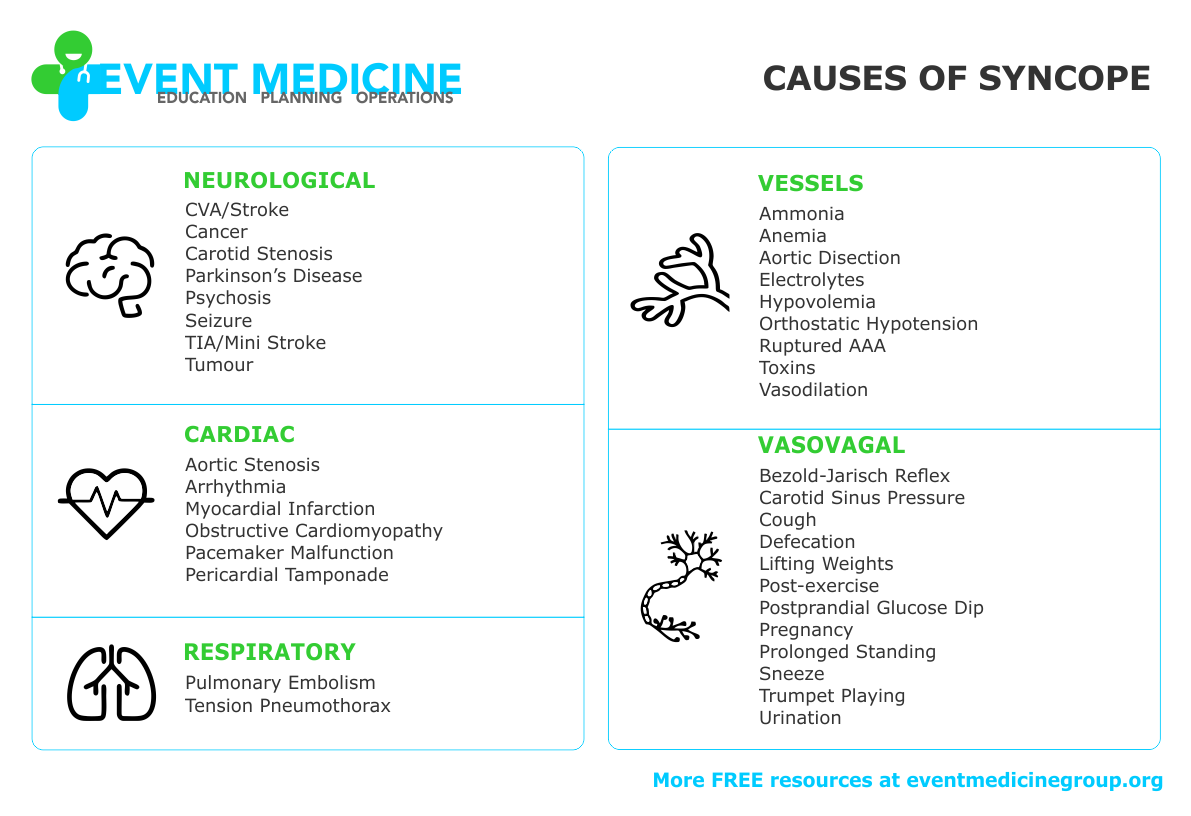
CAUSES OF SYNCOPE
Fainting and temporary loss of consciousness can be a sign of a serious medical emergency... or not.
Use this infographic to help work through differential diagnosis for syncopal episodes.
CAUSES OF ALTERED MENTAL STATUS
AEIOU TRIPS - a detailed list of differentials to consider for patients with altered mental status. From confusion and disorientation through to completely unresponsive, work through this list of medical and traumatic causes to rule in or out possible causes.
SIX DEADLY CAUSES OF CHEST PAIN
PETMAC
Six deadly causes of chest pain:
1. Pulmonary Embolism
2. Esophageal Rupture
3. Tension Pneumothorax
4. Myocardial infarction
5. Aortic dissection
6. Cardiac Tamponade
BECK'S TRIAD
Acute cardiac tamponade - three distinct 'D' signs indicating a fluid build up around the heart and a decrease in cardiac function.
Distant heart sounds
Distended jugular veins
Decreased blood pressure
CUSHING'S TRIAD
The body's ability to compensate from brain swelling cascades a spiral dive with increased systolic blood pressure, bradycardia and bradypnea.
TRAUMA TRIAD OF DEATH
After a serious traumatic injury, a patient may experience a combination of hypothermia, acidosis and coagulopathy resulting in a positive feedback loop leading to mortality.
OPIOID OVERDOSE TRIAD
Remember the acronymn CPR for the three signs of an opioid overdose such as heroin, fentanyl, or oxycodone (to name just a few).
Consciousness Decreased
Pinpoint Pupils
Respiratory Depression
Download Opioid Overdose Triad PDF.
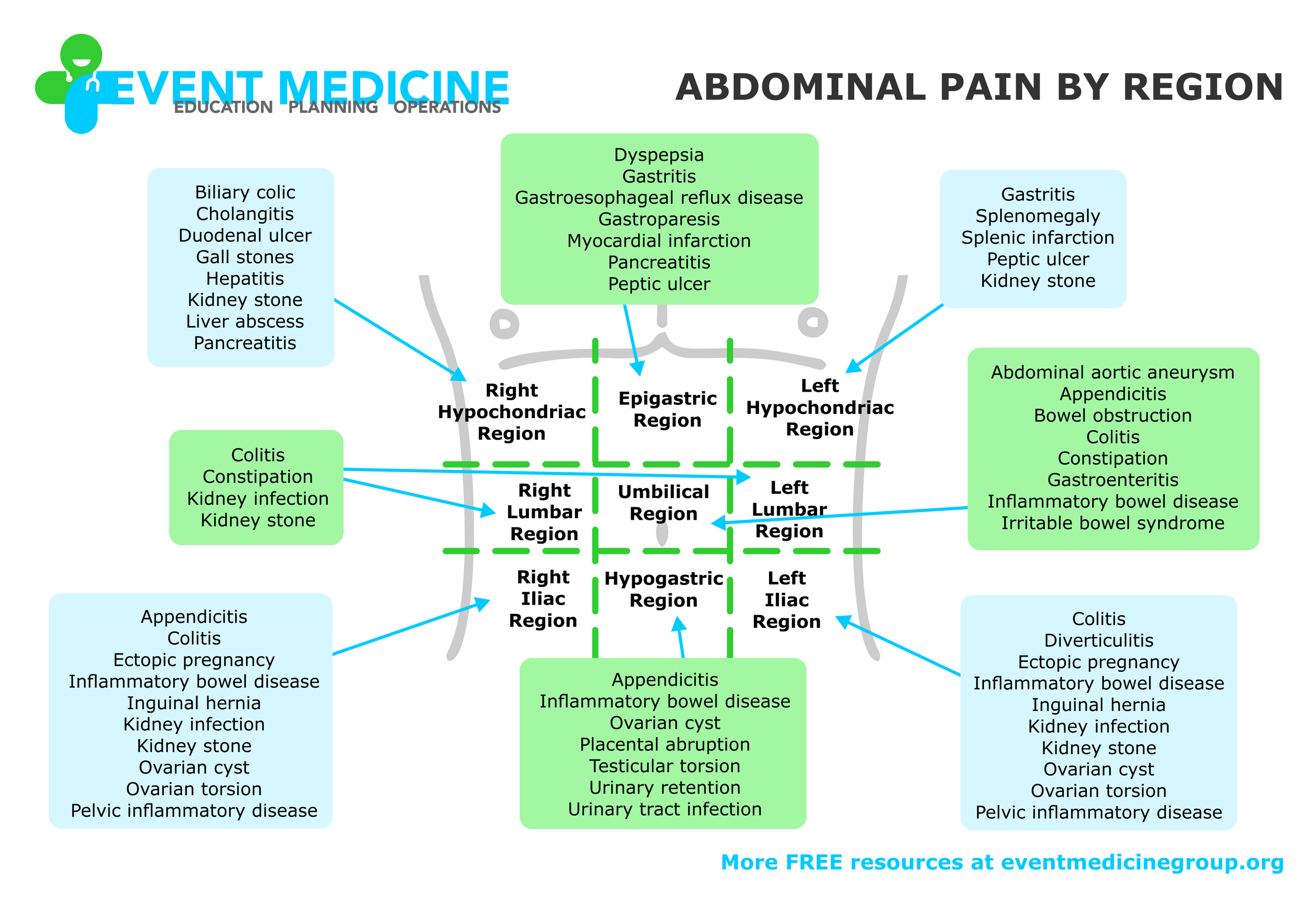
ABDOMINAL REGIONS
Identify patient complaints by region. Right Hypochondriac Region, Left Hypochondriac Region, Epigastric Region, Right Lumbar Region, Right Iliac Region, Left Lumbar Region, Left Iliac Region, Hypogastric
Region, and Umbilical Region.
This is a more precise method of identify abdominal areas compared with quadrants.
ABDOMINAL PAIN BY REGION
Identify medical complaints by the region pain is felt.
FAST SIGNS OF STROKE (FOR MEDICS)
Know the signs of stroke. Learn the FAST mnemonic for medics (it’s a bit different from the layperson).
FACE
Look at the patient square on and ask them to smile. Is everything equal or is there any drooping, drooling or uneven smile?
ARMS
Ask the patient to extend their arms out in front at shoulder height, palms up. Have them close their eyes and hold their arms in position for 15-20 seconds. Assess for arm drift.
SPEECH
Ask the patient to repeat a sentence to determine if they are able to speak without difficulty or slurring.
TIME
When did the symptoms start? Determine when was the last time the patient was confirmed as symptom-free. Determining if this was sudden, gradual or if any symptoms have resolved over time are also key findings to be recorded and reported.
One of the most important diagnostic steps with a suspected stroke patient is to check their blood glucose level. If the patient had a previous stroke, low blood sugars can manifest with similar symptoms. This can also occur in patients who have no stroke history and someone can also be suffering a stroke and hypoglycemia!
ANATOMY OF THE HAND (EXTERIOR)
Use this guide to identify key areas of the hand to enable more accurate reporting of hand injuries, deficits and treatments.
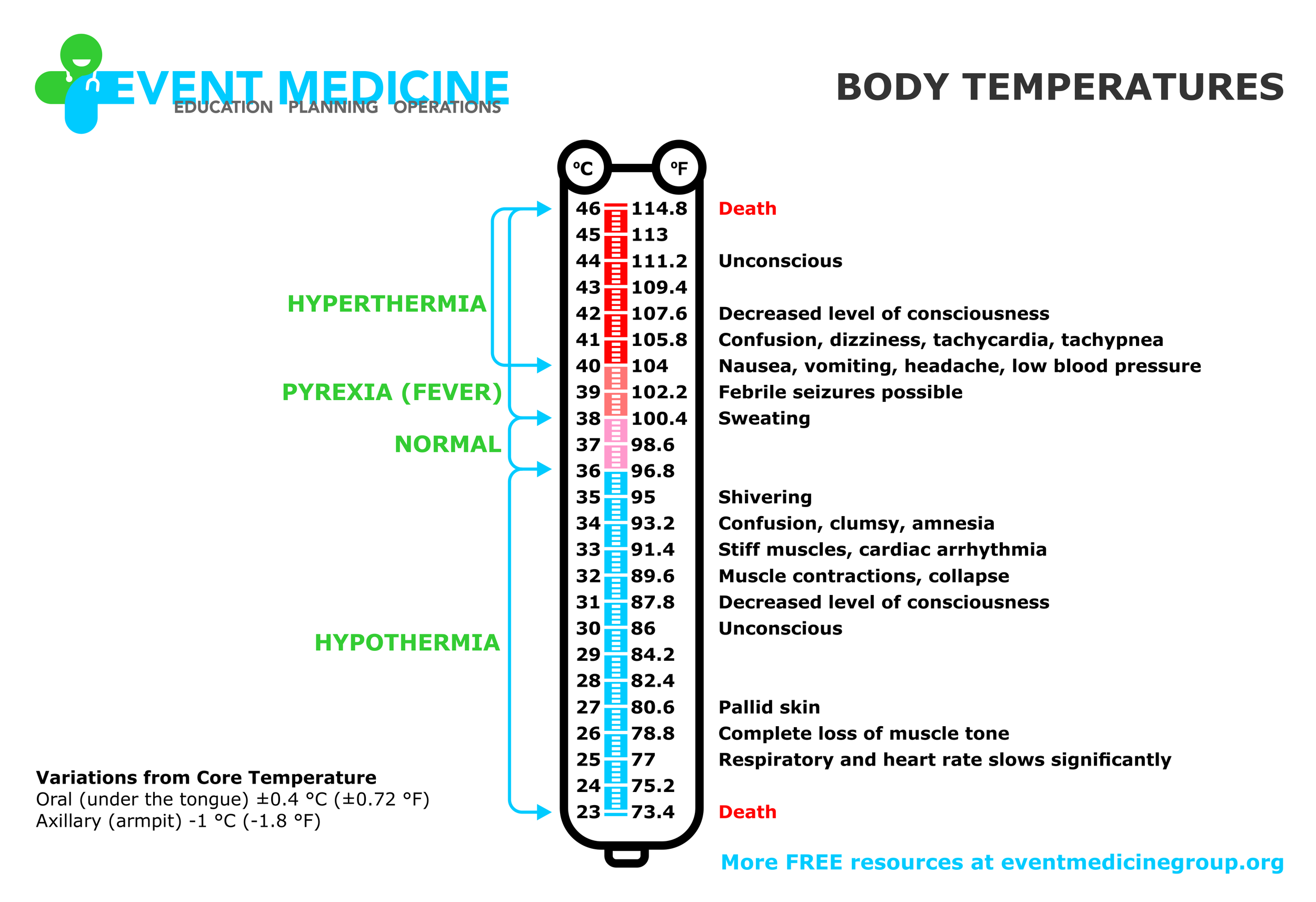
BODY TEMPERATURES
How hot is too hot? How cold can you get?
Learn about the signs and symptoms patients can exhibit based on changes to their core body temperature.
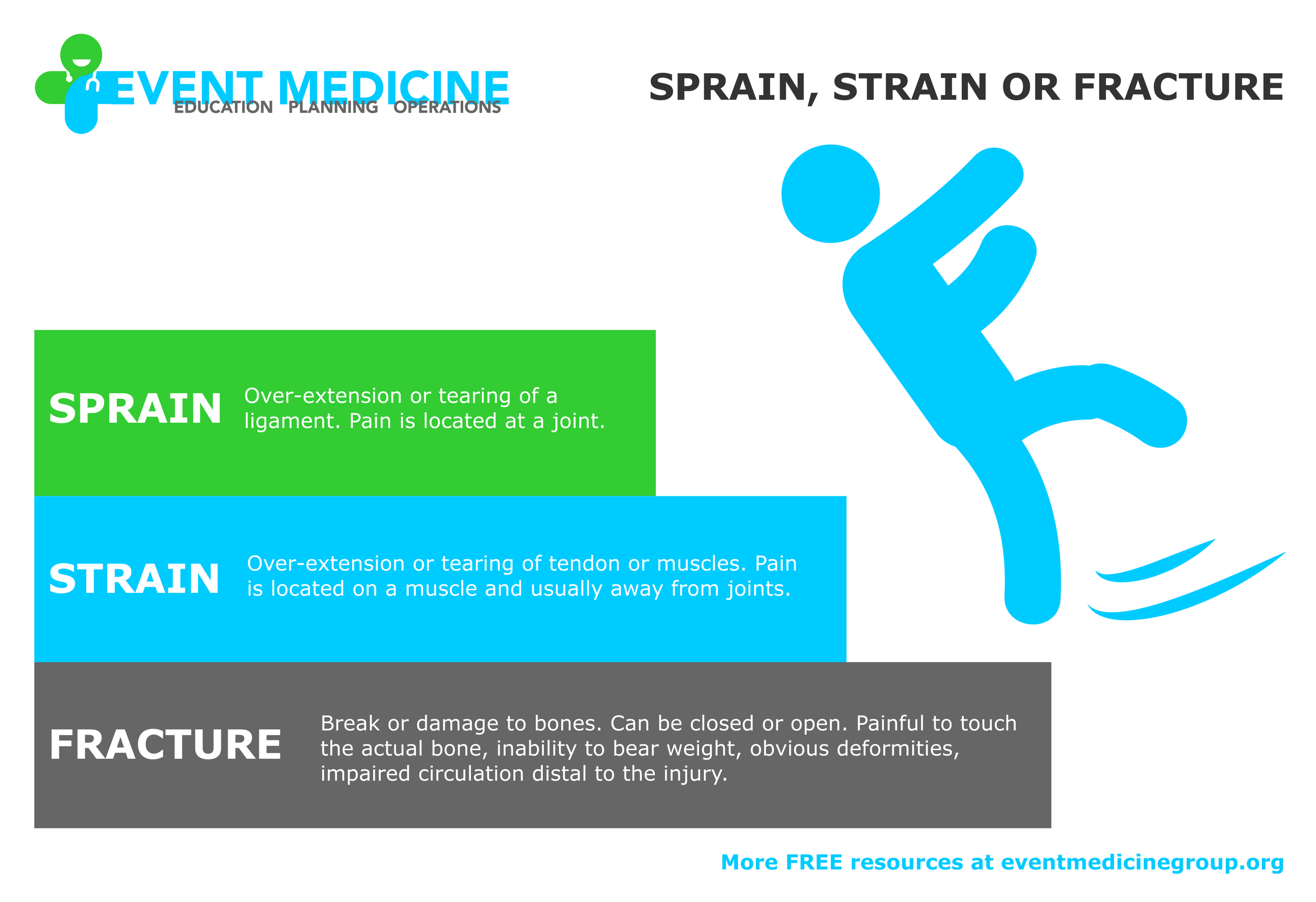
SPRAIN, STRAIN OR FRACTURE
How do you tell if a patient has sustained a sprain, strain or fracture?
Sprains are ligament related, strains are muscle or tendon related, and fractures are bone related.
Sprains typically occur at the site of a joint where a ligament is torn or stretched. Think of ankles or wrists.
Strains are usually located away from a joint and relate to the muscle or the tendon holding a muscle to a bone becoming damaged. Think of leg muscles or backs.
Fractures are when a bone is damaged. There may be deformity or poor circulation beyond the fracture. The pain is localized to the actual bone especially when touched.
It can be hard to tell the difference and sometimes the pre-hospital care doesn't require a definitive diagnosis but fractures must be immobilized to prevent further damage and can become life or limb threatening.